Neural Shopping Networks

A New Era of Retail Reactivity
It is Winter, 2150. A major clothing retailer is preparing for the big launch of their latest collection of adaptive climate suits. These suits automatically adjust to provide heat, cooling, or sweat wicking to the wearer. They even work with the climate of Mars and have become especially popular with the citizens of the Mars colony. As part of their preparations, the brand is conducting thorough inventory forecasting to ensure it has enough product on hand in its warehouses and retail centers across Earth, the Moon, and Mars. Traditional analytics would dictate that the brand should base their inventory on their previous product launches on Earth — but that type of forecasting hasn’t been relevant in years.
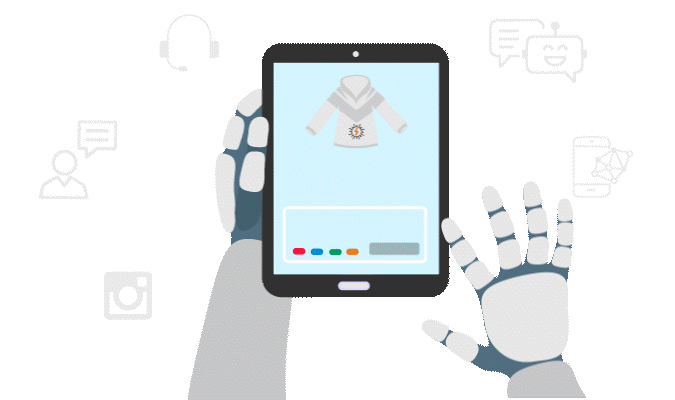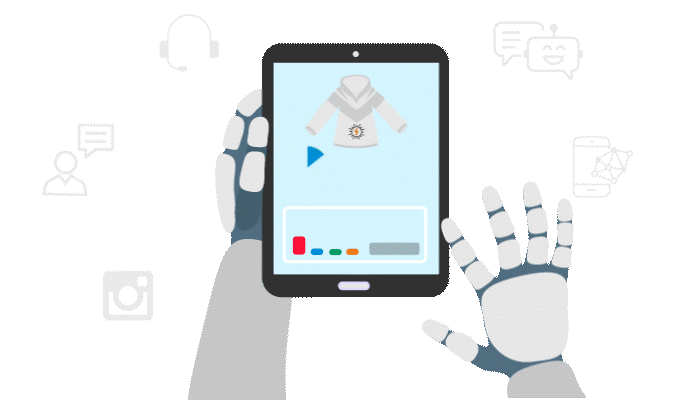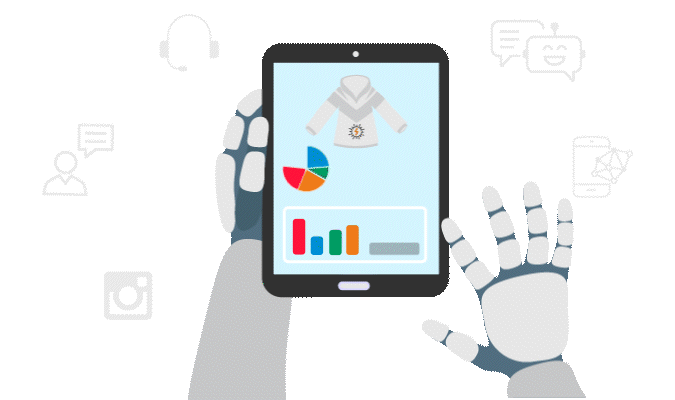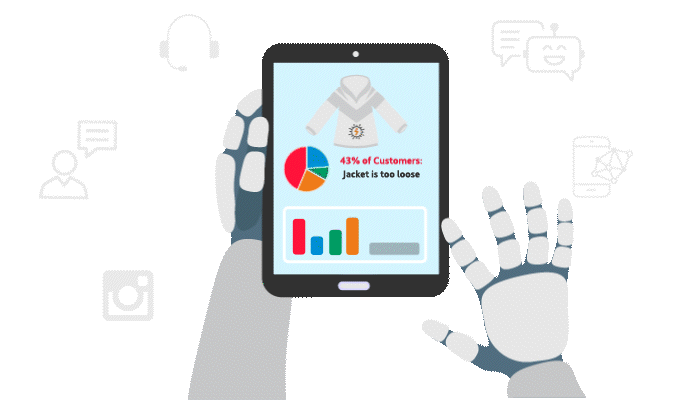
This interplanetary retailer relies on neural networks to analyze customer feedback coming from millions of customers. The network analyzes conversations with the retailer’s AI customer service bot, posts on interplanetary social media, conversations on large language models (LLMs), and more. The neural network analysis reveals a valuable insight: customers previously complained that the fit on the climate-controlled suits was too loose, which caused the climate-control functionality to not work properly. Social media monitoring also shows an increase in posts mentioning “easy” or oversized fits.
The retailer quickly makes changes to the climate-controlled suits to tighten the fit ahead of the latest launch. They perform additional quality control checks to make sure all climate-control functionality is working properly before products hit shelves.
This season-saving shift would not have been possible without the neural network’s ability to take in multiple unstructured data points and surface conclusions that traditional analytics tools may have missed.
Neural Network Know-How
Neural networks are advanced machine learning systems that mimic the structure and function of the human brain to identify patterns in large pools of data. They are the foundation upon which popular large language models are built, but their function can extend well beyond text processing. Retailers can leverage neural networks to personalize their marketing efforts and draw deeper insights, going beyond traditional customer segmentation to predict customer actions and offer more adaptable shopping experiences.
Even without the advanced analytics of a neural network, retailers already have a wealth of data at their disposal. Customer emails, website clicks, ad-driven traffic, social media engagements, purchase histories, conversion rates, product reviews, inventory numbers — the list goes on. Neural networks empower retailers to further capitalize on this information by transforming complex, unstructured data into deep, data-driven insights. Unlike traditional analytics, neural networks do not require complex standardization and organization. They can also learn and adapt, allowing retailers to move beyond static reports and analyze the full customer journey, creating a multidimensional view of each individual shopper.

These capabilities allow retailers to better improve and customize their products. Advanced sentiment analytics can shed light on emotional undercurrents in customer feedback that may have otherwise gone unnoticed. For example, instead of relying on static star ratings for a given product, neural networks can examine written reviews for common themes that cut across rating tiers. A collection of positive reviews may still contain valuable feedback about the item’s quality, and a collection of seemingly disparate negative reviews could contain a hidden throughline that helps a retailer diagnose and solve a problem.
Meanwhile, predictive inventory management functions can forecast a demand spike by automatically combining data like website traffic, social media engagements, and emerging purchasing trends. By getting this information earlier, retailers can dynamically adjust their production levels and warehouse inventories before orders start flowing in.
Other functions move beyond data and provide new and enhanced experiences for shoppers. Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs), for example, rely on neural networks to create high-quality three-dimensional reconstructions based on two-dimensional images. Retailers can use NeRFs to let digital customers see how a product, such as a piece of furniture, will look and feel in their own space. When customers know exactly what they are purchasing, they will be less likely to return an item and more likely to buy from the same retailer again in the future.
But, for all their advantages, neural networks integration requires thoughtful preparation. Retailers will need to support the substantial computational demands that neural networks bring, as well as navigate strict data privacy rules and best practices.
Digital Marketing's new dilemma: progress vs. privacy. Explore how retailers are advancing digital marketing while safeguarding user privacy in our 60-Second Retail Podcast: Can Digital Marketing & User Privacy Coexist?
Neural Network Head-Scratchers
Before neural networks can go mainstream, retailers will have to navigate several data infrastructure challenges, computing hurdles, regulatory compliance issues, and privacy imperatives.
While their core advantage is their ability to analyze unstructured data, neural networks still need a foundational structure for data categorization. For retailers, that means sorting data into broad subgroups to help the neural network understand what it is reading (denoting domains such as “feedback” or “inventory levels”). Retailers will also need to upgrade their existing data infrastructure to support data reliability and freshness, ensuring their information is accurate and up to date.
Giving customers as many avenues as possible to provide feedback wherever they shop — online, in-store, or in-app — can help ensure that the data available to a neural network is regularly updated and accurately reflects customer sentiments. Traditional product reviews are always essential, but as retailers introduce new ways of shopping — through NeRFs for example — customers should also be able to share how they feel about these experiences. Retailers will also need to implement automated systems to track certain inputs, such as warehouse inventory levels, to keep data current. Finally, retailers will need a centralized repository to store this data over the long term, providing the system with a wealth of information to look back on as it searches for trends.
Making use of all this information requires significant computational power, likely more than most retailers’ current systems allow for. If a retailer is planning to leverage neural networks to support NeRFs, which are even more resource-intensive than pattern recognition, those power demands can become even greater. This hurdle represents the largest barrier to adoption. The cost of building and maintaining suitable power infrastructure and server capacity to run a neural network in-house could be prohibitive for all but the largest companies. Smaller and mid-size retailers will need to seek out strategic partnerships with external vendors and cloud providers. They will also need to be able to scale those arrangements up or down during peak and low seasons, as their data and information demands evolve.
On the regulatory side, certain jurisdictions, such as the European Union (EU), apply greater scrutiny in their technology and privacy regulations. As another example, California’s Delete Act mandates the creation of a centralized deletion platform where users can request their data be deleted by all registered data brokers. Retailers operating in these markets will need to tailor and scope their neural network implementation to avoid running afoul of these and any other regulations that govern consumer data usage. For instance, real-time behavioral analytics in stores may be limited by laws that define specific use cases or storage time for closed-circuit television (CCTV) footage. In other cases, data collection efforts must be accompanied by clearly articulated permission structures that supply customers with notices covering the purpose, scope, and duration of data use.
Guarding against model bias will also be crucial. Neural networks are best trained on diverse data sets that represent a wide array of consumer profiles. Any decisions made based on a model’s recommendations should be vetted prior to implementation, and outputs should be continuously tested for hidden biases that could harm a retailer or its customers. The presence of bias may require a retailer to reweigh or resample its data or adjust the neural network’s underlying algorithm.
While these challenges are significant, they are not insurmountable. Retailers interested in neural networks should take a methodical approach to adoption. A strong data governance foundation is a critical prerequisite, as are compliance and privacy considerations. Baking these pillars into workflows, technology updates, and decision-making processes from the beginning can help retailers future proof their businesses and set themselves up for long-term success.
See how retailers are solving privacy puzzles - one case study at a time. Explore BDO's portfolio of real-world wins in privacy and compliance: Overcoming Retail Compliance Challenges.
How BDO Can Help: Avoiding Compliance and Security Pitfalls
Neural networks may sound like science fiction, but they are already here. Retailers need a plan for neural network adoption in order to future-proof their business. Some retailers are already leveraging LLMs within their operations to support customer inquiries and other interactions. Deploying neural networks for data analysis and product rendering represents the next stage of this evolution. As neural networks become more accessible and usable – whether 5 years from now or 50 – the industry will likely see an adoption spike similar to the proliferation of LLMs in recent years.
BDO’s AI Services professionals can help you manage and structure your data and set up automations to maintain data freshness so that inputs into AI systems are clean and accurate. We can help evaluate your current infrastructure and develop responsible AI governance frameworks that support effective neural network integrations. In addition, BDO’s Privacy and Data Protection Services professionals can help retailers like you keep abreast of evolving AI and data privacy regulations before and during adoption. Our team can help, institute bias prevention testing that supports complaint, fair, and useful outputs, as well as work with your team to establish data protection parameters that safeguard sensitive customer data coming from various channels.
For retailers who are ready to take the next step and upgrade their systems, our teams can assist you in assessing your cloud computing needs and building a roadmap to help achieve neural network maturity.
Don’t Just Predict the Future—Shape It
Explore what neural networks can do for your business.