BDO Knows: Transaction Advisory Services
IT Due Diligence – An Essential Element in the M&A Due Diligence Process
Performing IT due diligence prior to a merger or acquisition has become an essential step to ensure better valuation, financial modeling, and risk mitigation. The primary objective of IT due diligence is to determine if there are insurmountable risks which could impact the transaction or post-transaction integration. The depth and focus of the due diligence should be tailored to the goals of the transaction.
Assess from a CIO Perspective
The due diligence process looks at the IT organization through the lens of the Chief Information Officer (CIO). The need to assess an IT organization in a few days or weeks requires a tailored and systematic approach that focuses on essential areas. By identifying key issues and risks early on, acquiring companies can strategize and develop mitigation options. If analysis indicates substantial impact on the operating model, this information may be leveraged during negotiations.
Benefits of IT Due Diligence
Variations in technologies and levels of sophistication between the acquiring IT organization and the target company can create risks both to effective integration and future operations. Focusing on IT due diligence allows for the acquiring organization to gather information on potential synergies, identify any security concerns and evaluate IT staff and structures. A comprehensive and well-managed process should:
-
Evaluate overall IT strategy effectiveness, including processes, project portfolio, support structure, and alignment to business goals.
-
Identify operational improvements, synergies or cost savings opportunities such as rightsizing the IT support model and vendor contracts.
-
Assess capability to integrate core business processes and systems (e.g., ERP, supply chain management, CRM).
-
Assess the security and controls framework to minimize exposure to costly litigation for data exposure or theft.
-
Evaluate the health of IT infrastructure to determine ability to scale, integrate, or maintain current operational demands.
-
Identify single points of failure that require mitigation planning.
-
Identify hidden or buried IT costs resulting in a higher than expected operating model.
-
Identify deferred or unplanned software license costs, which may create post-transaction investment.
-
Identify transition issues to consider post-transaction, which would help to assess the cost and timing of integration.
-
Evaluate intellectual property, which may impact the valuation of the target company.
The Approach
An IT due diligence team should deploy a consistent due diligence framework to ensure that IT capabilities are prioritized and adequately assessed. The framework targets key areas of risk and is structured to be able to support the larger due diligence effort. The IT team should work closely with the larger transaction team to plan, execute and deliver information to inform the final decision.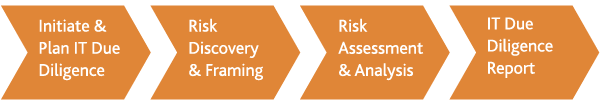
-
Initiate & Plan IT Due Diligence: During this phase the team validates the project vision, strategic direction and goals of the transaction. A communications and project plan is established to ensure an adequate delivery and reporting cadence.
-
Risk Discovery & Framing: During this phase a tailored request list is developed and communicated to the target company. The requested items should focus on the critical success factors. Common areas to include are IT personnel and organization, IT strategy, tools and applications, architecture and infrastructure, IT governance and controls, and IT financials. Information is gathered and assessed through data requests, interviews, and onsite visits.
-
Risk Assessment & Analysis: During this phase a comprehensive risk assessment is developed based on technology or operational gaps which may impact the transaction or post-deal integration. Whenever possible, mitigation options should be identified along with associated costs.
-
IT Due Diligence Report: During the final phase a summary of key findings and recommendations should be developed and communicated. The focus areas and recommendations should tie back to the goals of the transaction.
Tips, Tools & Techniques
Tools
The implementation of adequate tools during the assessment should ensure consistent results. These tools can be simple templates using Excel and Word, but there are also commercial products available. The most common templates used are a request list (also referred to as a checklist), issue and risk log, meeting/interview minutes, and the IT due diligence report.
Tailored Request List
The IT request list is a critical tool used during the due diligence process. It is tailored based on deal strategy and helps facilitate the sharing of essential information to be evaluated. It may be useful to pare down the initial data inquiry as a long list of items may overwhelm the target company and may create unnecessary delays. In addition, feedback on the initial request items often allows a more meaningful and focused follow-up request. As request items are being assessed, risks are identified, prioritized, and assessed.
Reporting
The IT due diligence report, or report of key findings, should provide a summary of the target company, context of the transaction, and the approach used to perform the assessment. A summary of key findings and risks should be included, which identify potential impact, mitigation options, cost implications, and a recommended approach. The report should be written in a manner that can be understood by non-IT professionals. If technical terminology or acronyms are used, a glossary should be included.
Understanding the goals of the transaction and following a consistent yet tailored approach should maximize the value provided through IT due diligence.
SHARE