Economic Considerations of Eliminating Restaurant Tips
Is the U.S. restaurant tipping model on its way out? Amid concerns over whether compensation for back-of-the-house and front-of-the-house employees is fair and how the push for raising minimum wage will impact cost-cutting measures, the tip reform movement is stirring up controversy. Earlier this month, Danny Meyer, CEO of Union Square Hospitality Group, made waves in the industry when he called tipping a “broken system” and announced that his restaurants would phase out tipping by January. The pros and cons of this consideration have impact from the board room to the dining room, and servers, cooks, owners and customers have a stake.
But what about the economic impact? Reporting tips for tax purposes is one of the most complex requirements for restaurants and their employees. Here is a look at the potential effects of eliminating tipping:
Owners Adjust for Higher Wages, Lose the Tip Tax Credit
Federal law allows restaurants to pay servers $2.13 per hour with the server’s tips expected to meet or exceed federal minimum wage requirements. Some states—like New York which will have a $15 minimum wage for fast food workers in 2016—require a higher minimum wage. Additionally, there is a federal income tax credit (IRC 45B) that the restaurant can take for all tips reported by the server in excess of $5.15 per hour. This gives the restaurant an incentive for encouraging their employees to report all their tips. In a non-tipping environment, restaurants would have to pay higher wages and higher employment taxes, but would have a larger deduction for the increased wages and payroll taxes.
The federal FICA tip credit has been a significant benefit for a number of restaurants over the years. Restaurants that are considering changing to a no-tipping policy may be giving up a substantial tax benefit, and need to take that into account when setting menu prices or additional service charges to help finance the increase in non-tipped wages.
Some fine dining establishments who have eliminated tipping have added a service, hospitality or administrative charge, while others have raised menu prices to compensate. It's important to note that service charges do not constitute tips for the purposes of the federal FICA tip credit.
Employees Gain Predictability, but not Guaranteed Higher Earnings
Servers are required by law to report all tips, but the IRS has suggested that as much as 40 percent of restaurant tips are not reported. If this is true, many employees are paying less income and employment tax than they should in a tipped environment. In a non-tipped establishment, employees receive wages which may or may not be as much as they earn in a tipping situation. Ideally, the non-tipped wage would create more predictability in employees’ income, eliminating the uncertainty associated with fluctuating tips from shift to shift. However, some will do better and some worse under a no-tipping model. Bonuses may be necessary to retain servers.
Calculation: Let’s take a look at a simple example of how the FICA tip tax credit works.
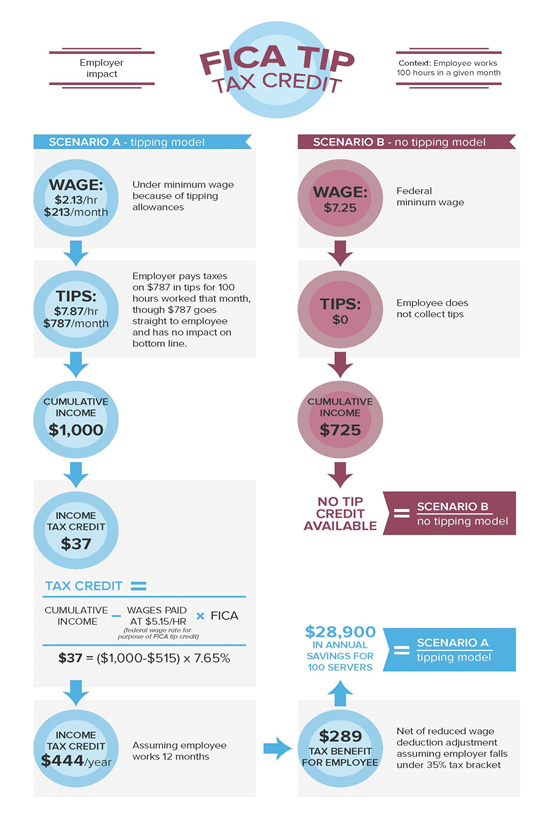
It remains to be seen whether the tip elimination trend will be a mere crest or a tidal wave of change in the restaurant industry. It is clear, however, that the business impact could be substantial, and restaurants would need to adapt practices accordingly. Even if restaurants and employees can thrive on a no-tipping model, how will customers react? Stay tuned to our blog in the weeks ahead as we explore the potential implications for players throughout the industry.
Have questions about the economic considerations of eliminating tipping? Contact Phil Hofmann at [email protected]. And be sure to keep up with the Restaurant practice’s latest thoughts by following us on Twitter at @BDORestaurant.
SHARE